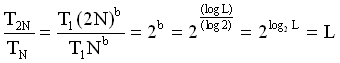Mgt 3325 -
Home Spring 2010
Email
to Dr. Lyons
PatLyons Home
Mgt 3325 -
Home Spring 2010
Email
to Dr. Lyons
PatLyons Home
[ Calendar12:20 |
1:25
| Class Participation AI | App of OM |
Table of Contents | Search ]
[ Ch 1 | 2 |
3 | 4 | 5
| 6 | 6S |
7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11
| 12 | 13 | 14
| 15 |
16 | 17 | | HW1 | 2 | 3
| 4 | | Career1| 2
| 3 | 4
]
[
SJU
|
TCB |
CareerCenter |
StudentInfo |
CareerLinks |
Internships ] [NYC Teaching
Fellows] [
SJU Closing ] [H1N1SelfAssessment]
Ch 11 - Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain's Strategic Importance
(p434)
- Def - Supply Chain - the facilities and activities involved in
producing and delivering a product (good or service) from suppliers (and their suppliers)
to customers (and their customers).
- Objective - maximizing value to the ultimate customer.
- The profound improvement in supply chain mgt is due to:
- The rapid flow of information among suppliers and customers,
- *The use of mgt science computer models to optimize operations.
- Note: 20 years ago, average purchase order (PO) was manual, and cost $50. Today,
average PO is electronic and costs $0.50.
- Supply Chain Facilities include - plants, warehouses, distribution
centers, service centers, retail operations.
- Supply Chain Activities include:
- Purchasing
- Material and financial transfers (Chs 12 - Inventory Mgt, 14 - MRP)
- Scheduling (Chs 13 - Aggregate Planning, 15 Short-term Scheduling)
- Transportation - shipping & delivery (Ch 8 - Location, TransLP)
- Customer service (Module D - Waiting Lines)
- Purchasing
(Supply Chain Economics, p436)
- Def - Purchasing - the acquisition of goods and services.
- Objectives of purchasing
- *Identify products that can best be obtained externally
Make-or-Buy Decision - Table 11.4, page 437.
- *Evaluate,
develop and determine the best price, supplier and delivery for those
products.
- Def - Internet Purchasing (also called e-procurement)
(p445) - purchasing that uses the Internet
to communicate orders. Part of
Enterprise Resource Planning Systems (Ch 14)
- Note: Ford, General Motors, and DaimlerChrysler set up a super auction
Internet site to buy $250 billion worth of parts each year. This cuts their cost by at least 10 percent,
reducing the price of building a car by $1,000. Parts account for $10,000 of the cost of a $20,000 car. (Reference:
"Believe All the Hype About B-2-B, It's the Real
Thing",
http://dailynews.yahoo.com,
Tech Headlines, March 3, 2000)
- Purchasing Responsibilities
(Vendor Selection, p447)
- *Vendor Evaluation
- Vendor Development - training vendor to ensure proper quality, delivery,
engineering changes
- *Negotiation of Contracts - use learning curves
(Module E below)
- Opportunities in an Integrated Supply Chain
(Techniques to enhance value, p442)
- *Vendor Managed Inventory - supplier delivers product directly to user department, not
stockroom. Example - car seat supplier delivers seats directly to production line.
- *Postponement - withholds customization to the product as long as possible.
Example - by moving the power supply out of the printer and into the power cord, HP can
ship printer anywhere in the world.
- *Drop Shipping - supplier ships directly to end consumer. Example - When customer
buys a Dell PC with HP printer, printer is drop shipped to customer. Dell never
holds printer.
- *Standardization - when possible, replace several similar products with one
standard product. Example, a company standardizes on Microsoft Word.
- Benchmarking Supply Chain Management
- Table 11.6 - Supply
Chain Performance - p452
| |
Typical firms |
Benchmark firms |
| Percent of late deliveries |
33% |
2% |
| Percent of rejected material |
1.5% |
.0001% |
| Number of shortages per year |
400 |
4 |
Learning Curves (Module E - page 782)
Def - Learning Effect - each time the production quantity doubles, the unit
production time is reduced by a constant rate.
Example - A production process follows an 80% learning curve where first unit
requires 100 hrs. Then:
- Second unit requires 100(.80) = 80 hrs
- Fourth unit requires 100(.80)2 = 64 hrs
- Eighth unit requires 100(.80)3 = 51 hrs
*Learning Curve - let TN denote the time to produce the N-th unit,
then:
TN = T1 N b
where b = (log L) /
(log 2) and
L = learning fraction.
Verification of learning property (for your information only)
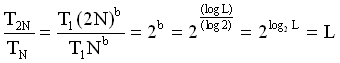 For N equal to a power of 2 (2, 4, 8, 16, . . . ), TN can be easily
computed without logs
For N equal to a power of 2 (2, 4, 8, 16, . . . ), TN can be easily
computed without logs
- If N = 2n , then TN = T1 Ln
- Example E2 - tugboat - page 786
T1 = 125,000 hours, L = 0.85. Find T4
Since 4 = 22, T4 = T1
L2 = (125,000) (0.85)2 =
(125,000)
(0.7225) = 90,312 hours
Do assigned HW
(This
page was last edited on
October 22, 2009
.)
 Mgt 3325 -
Home Spring 2010
Email
to Dr. Lyons
PatLyons Home
Mgt 3325 -
Home Spring 2010
Email
to Dr. Lyons
PatLyons Home