 Mgt
509
Home
Fall 2006
Email
to Dr. Lyons PatLyons
Home
Mgt
509
Home
Fall 2006
Email
to Dr. Lyons PatLyons
Home
[
Calendar | Photo | Class
Participation AI |
Application of Ops Mgt | Table of Contents |
Search ]
[
Chapter
1 | 2 | 3 |
4 | 5 | 6 | 7
| 8 | 9
| 10 | 12
| 13 |
14 | 15 | 16 | 17
| | HW1 | 2
]
[
SJU
|
TCB |
CareerCenter |
QueensEvents |
COACH |
CareerLinks |
MBAServices |
Internships ] [
ProjectLiberty ]
Ch 9 - Project Management
- Introduction
- Project
(p361)
- Def - one-of-a-kind production of a customized product that requires a long completion
time (from Ch6, p223).
- Examples - constructing a building, developing a new product.
- Elements of Project Management
(p363)
- Project team - organization can be:
- Temporary - individuals assigned from different departments within company and then
disbanded.
- *Permanent - Matrix Organization - two-dimensional structure with members from different
functional areas (dimension 1) assigned to various projects (dimension 2).
- Project Scheduling - determining
(p367):
- Activities - tasks which make up the project
- Precedent relationships - activities which must be completed before another activity can
start
- Activity time - time it takes to perform an activity
- Gantt Chart
- Popular tool for scheduling small projects
- Example - Fig 9.4, p368
*Critical Path Method
(p371)
- Def - Basic Critical Path Method (CPM) - a method to determine the activities which are
critical to completing a project on time.
- Example Fig 9.8 - building a house, p373
- designate activities with letters not numbers (reduces confusion).
|
Activity
|
Precedent
Relationship
|
Activity
Time (months)
|
A - Design house
B - Lay foundation
C - Order materials
D - Build house
E - Select paint
F - Select carpet
G - Finish work |
-
A
A
B, C
B, C
E
D, F |
3
2
1
3
1
1
1 |
- Construct Project Network
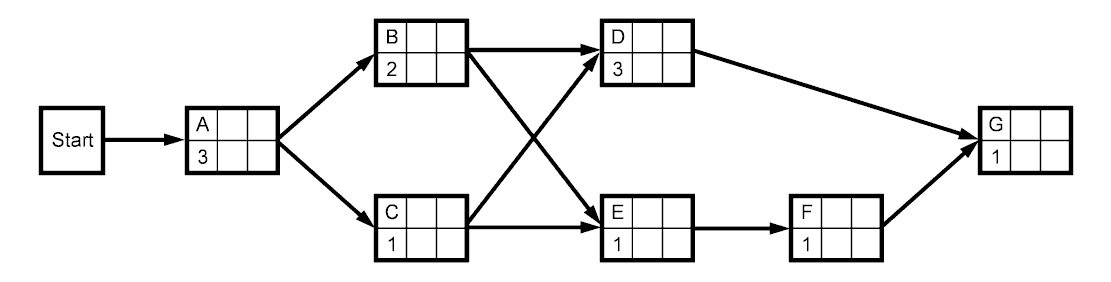
- Basic CPM Procedure
(p375)
- Compute earliest start (ES) time and earliest finish (EF) time for each activity
(forward pass)
- ES of activities with no precedent relationships = 0
- EF for a given activity = its ES + its activity time
- ES for a given activity = largest EF of the immediately preceding activities.
- Compute latest start (LS) time and latest finish (LF) time for each activity
(backward pass)
- LF of any final activity = the largest EF
- LS for a given activity = its LF - its activity time
- LF for a given activity = smallest LS of the immediately succeeding activities.
- Compute slack time for each activity: Slack = LS – ES
- *Identify the critical path. An activity is on the critical path if its slack time = 0.
Note: If an activity on the critical path takes longer than estimated,
then final date will be affected.
- Example - Fig 9.12 (continued)
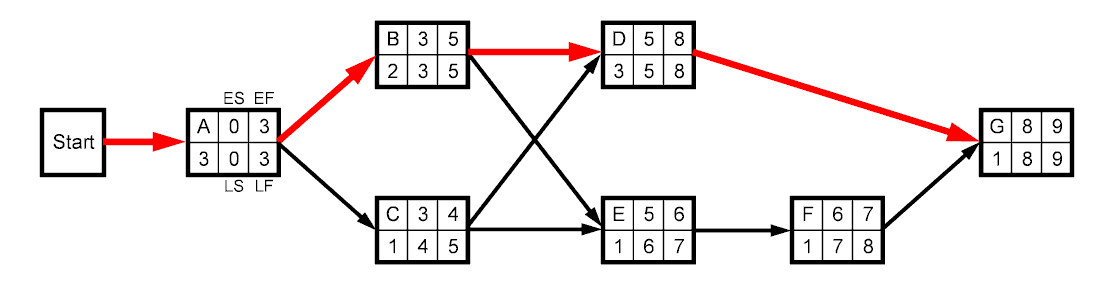
|
Activity
|
Slack = LS - ES
|
A
B
C
D
E
F
G |
0 - 0 = 0
3 - 3 = 0
4 - 3 = 1
5 - 5 = 0
6 - 5 = 1
7 - 6 = 1
8 - 8 = 0 |
Critical path: A, B, D, G
Do assigned HW - Problem 9-8.
(This page was last edited on
August 16, 2006
.)
![]() Mgt
509
Home
Fall 2006
Email
to Dr. Lyons PatLyons
Home
Mgt
509
Home
Fall 2006
Email
to Dr. Lyons PatLyons
Home 
